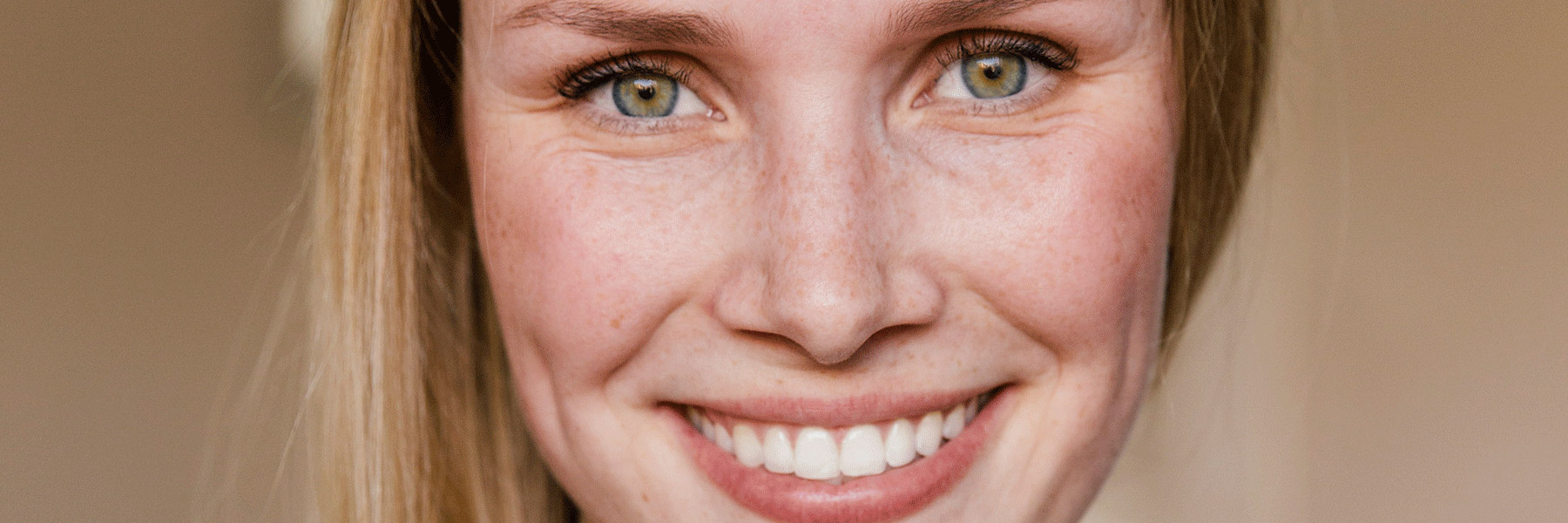
Some people with sensitive and reactive skin types have redness and small, visible vessels on their faces. These signs often appear temporarily, but they can become progressively worse and eventually permanent.
All about visible facial redness and visible vessels
Reading time : 5 min

What causes visible redness?
Redness or small visible vessels are skin symptoms caused by an abnormality in the face’s venous system, which is not working normally. Redness, with or without heating, is temporary or longer lasting.
Certain factors aggravate the condition:
- Experiencing drastic temperature variations (hot-cold);
- Consuming hot and spicy food, alcohol, etc.
Rosacea and couperosis, which is a form of rosacea, most often cause redness and visible vessels to appear on the face. But these aren’t the only causes. Certain dermatological diseases that cause dilated vessels stimulate couperosis and flushing can correspond to underlying diseases that must be explored. In addition, certain medications can cause dilated vessels to appear on the face or increase those already present. A dermatological consultation is therefore warranted if there are doubts.
What are the symptoms of couperosis?
Couperosis is a dilation of small superficial skin vessels.
The network of superficial vessels forms a "capillary system" made of reddish linear lines on the face. Some of this network’s parameters may vary, depending on the person and his/her skin type, the age of the process, and the internal or external temperature or changes in temperature. The vessels are more or less wide and their color ranges from bright red to purple or even bluish.
The topography varies but is usually relatively symmetrical. Sometimes only the nostrils are affected, but the cheekbones or the cheeks, more generally, are the most common area affected. However, the whole face may be affected.
Logically then, the general term describing the condition mid-way between the two variants is erythro-couperosis.
A spider angioma may be observed with couperosis. This is a star-shaped vascular tree containing a more or less raised central red spot.
In most cases, couperosis is not related to any underlying disease; it appears slowly and progressively. It is a form of rosacea.
Flushes may occur before couperosis appears. The other signs of rosacea are erythrosis and possibly red papules (small spots) or pustules. Alcohol consumption does not cause couperosis or rosacea.
What causes couperosis?
- The exterior weather conditions play a role, since exposure to bad weather, the sun and outside temperature variations experienced when working or pursuing a hobby can cause it to appear.
- Alcohol consumption does not cause couperosis or rosacea.
Who is affected by couperosis?
People with fair, thin skin are more often affected.
Do you know your skin concern?
What are the symptoms of rosacea?
Rosacea is a common dermatological condition that only affects the face, particularly the nose, cheeks, forehead and chin. The eyes may be affected (ocular rosacea) but this is rarer. Rosacea is not acne, and the term “acne rosacea” which is sometimes used, is being phased out. This visible skin condition is often psychologically challenging because it causes disfiguration and is frequently mistaken for a sign of chronic alcoholism.
Three different forms, three symptom types
1/ Erythrosis and couperosis
It appears as redness on the face, with or without couperosis (small dilated vessels on the cheeks and nose). This redness may sporadically be accompanied by sensations of hot flushes on the face that quickly dissipates.
2/ The papulo-pustular form
Erythrosis is combined with flare-ups of pimples that resemble acne (red spots and small pustules, but no comedones), still found exclusively on the face
3/ The hypertrophic form
This form characterized by a large, bumpy nose is much rarer and almost exclusively affects men. It is called rhinophyma and is not related to alcohol consumption, unlike what many people think. All of these symptoms often cause significant everyday discomfort and impaired quality of life.
What causes rosacea?
- Genetic factors: women with fair skin from northern European regions are particularly affected
- External environmental factors: exposure to UV rays, temperature changes (certain occupations are more exposed)
- Stimulant use: Such as alcohol, spices are dominant in the onset of rosacea
- Abnormal facial function: seems to be the main cause of flushing
- A small parasite: Demodex folliculorum, typically found in the skin, appears to play a significant role. Here it causes an inflammatory reaction
Who is affected by rosacea?
Rosacea is three times more common in women than in men, and people with fair skin are the most affected.
Symptoms often appear around the age of 30, but it has a peak age of around 50.
A frequent characteristic of rosacea is that it occurs in sensitive skin.
What should I do?
A dermatologist is the best resource for identifying skin disorders, finding the cause of your skin issues, and developing an adapted treatment. Please consult your dermatologist, doctor or pharmacist so that they may best advise you on your personal skin regimen.
Preventive treatment includes limiting triggering factors, such as temperature changes, UV exposure, hot drinks, spicy dishes, coffee and alcohol. Alcohol does not trigger this condition, but consuming it may exacerbate symptoms.
If flushing occurs, doctors recommend letting an ice cube melt in your mouth during the first few minutes of flushing.
Certain medicated treatments may be prescribed by the doctor.That said, rosacea is not cured by these treatments because it progresses in flare-ups and local treatments need to be maintained continuously. Redness is difficult to treat; however, laser treatments are particularly beneficial.
The preferred treatment for couperosis is laser treatment. This technique has significantly changed the management of this problem. There are several types of laser treatments.
Dermo-cosmetic care can be useful to help visibly improve your skin and contribute to visibly minimize the appearance of visible redness; they should be moisturizing, soothing, non-occlusive and intended for sensitive skin. It is also important to use appropriate cleansing products, limiting contact with tap water. Photoprotection is also recommended. In some cases, redness concealing creams may also be helpful. (They contain green pigments that neutralize redness.)